contraindication
AURYXIA® (ferric citrate) is contraindicated in patients with iron overload syndromes, e.g., hemochromatosis
warnings and precautions
- Iron Overload: Increases in serum ferritin and transferrin saturation (TSAT) were observed in clinical trials with AURYXIA in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on dialysis treated for hyperphosphatemia, which may lead to excessive elevations in iron stores. Assess iron parameters prior to initiating AURYXIA and monitor while on therapy. Patients receiving concomitant intravenous (IV) iron may require a reduction in dose or discontinuation of IV iron therapy
- Risk of Overdosage in Children Due to Accidental Ingestion: Accidental ingestion and resulting overdose of iron-containing products is a leading cause of fatal poisoning in children under 6 years of age. Advise patients of the risks to children and to keep AURYXIA out of the reach of children
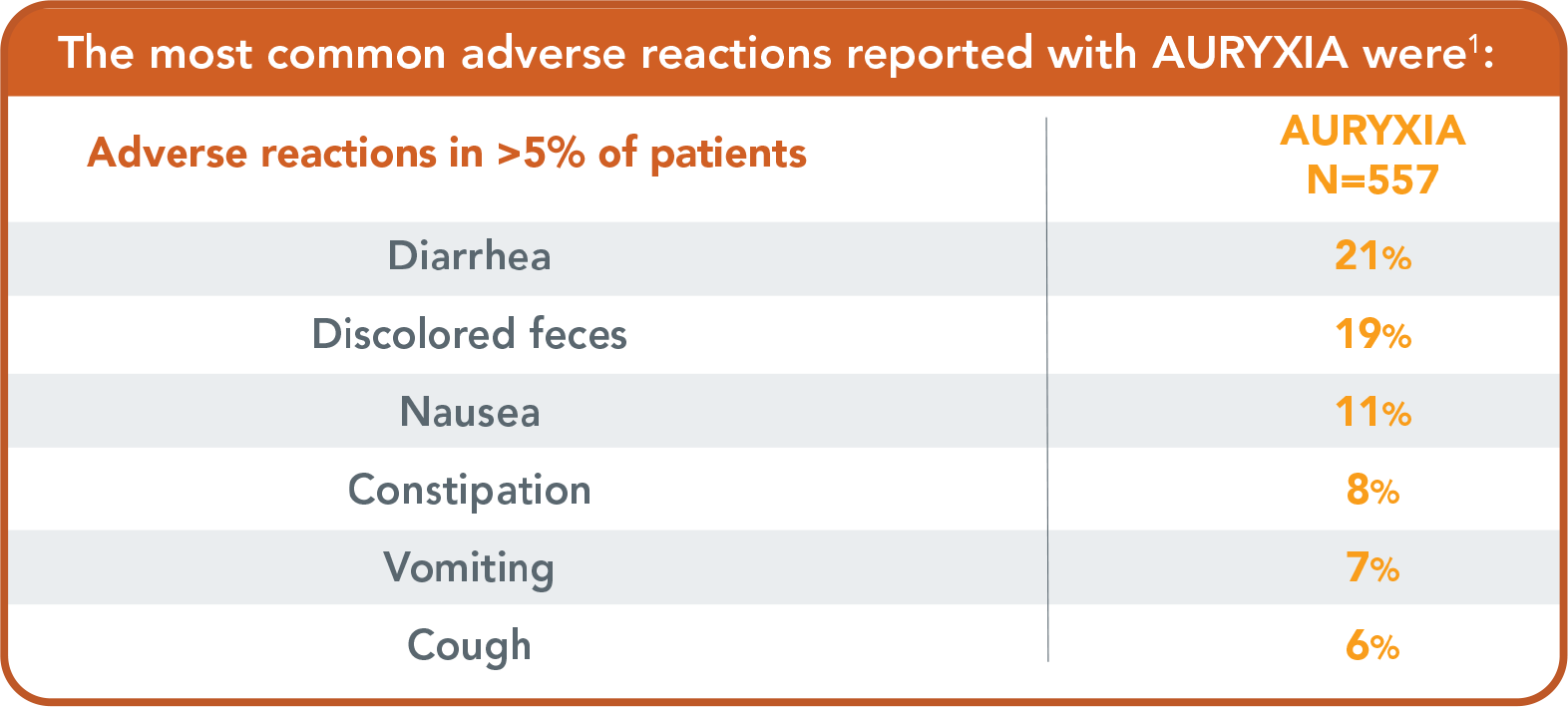
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions reported with AURYXIA in clinical trials were:
- Diarrhea (21%), discolored feces (19%), nausea (11%), constipation (8%), vomiting (7%) and cough (6%)
specific populations
- Pregnancy and Lactation: There are no available data on AURYXIA use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage. However, an overdose of iron in pregnant women may carry a risk for spontaneous abortion, gestational diabetes and fetal malformation. Data from rat studies have shown the transfer of iron into milk, hence, there is a possibility of infant exposure when AURYXIA is administered to a nursing woman
indication
AURYXIA® (ferric citrate) is indicated for:
- The control of serum phosphorus levels in adult patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis
To report suspected adverse reactions, contact Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. at 1-844-445-3799
Please see full Prescribing Information
References:
1. AURYXIA® [package insert]. Cambridge, MA; Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 2. KDIGO 2017 Clinical Practice Guideline Update for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney International Supplements. 2017;7(1):1-59. Accessed 08-30-2022. https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/2017-KDIGO-CKD-MBD-GL-Update.pdf 3. Data on File 38, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 4. Data on File 1, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 5. Data on File 34, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 6. Data on File 32, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 7. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42(4 Suppl3):S1-S201. doi:10.1053/S0272-6386(03)00905-3 8. Umanath K, Sika M, Niecestro R, et al; for Collaborative Study Group. Rationale and study design of a three period, 58-week trial of ferric citrate as a phosphate binder in patients with ESRD on dialysis. Hemodial Int. 2013;17(1):67-74. 9. Data on File 37, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 10. Data on File 33, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 11. Chiu YW, Teitelbaum I, Misra M, de Leon EM, Adzize T, Mehrotra R. Pill burden, adherence, hyperphosphatemia, and quality of life in maintenance dialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(6):1089-1096. doi:10.2215/CJN.00290109 12. Data on File 4, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 13. Data on File 11, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 14. Data on File 6, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 15. Data on File 10, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc. 16. Umanath K, Jalal DI, Greco BA, et al; for Collaborative Study Group. Ferric citrate reduces intravenous iron and erythropoiesis-stimulating agent use in ESRD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26(10):2578-2587. 17. Data on File 2, Akebia Therapeutics, Inc.